
The method was trained using 3155 records and tested on 1277 hidden records. Generated features are processed using logical rules and probability assessment, a prototype of a new machine-learning method. The largest group of features is extracted from the statistical properties of the averaged shapes other features are extracted from the symmetry of averaged shapes, and the last group of features is independent of S1 and S2 detection. A total of 53 features are extracted from the data. The averaged shape of the S1/S2 pair is computed from amplitude envelopes in five different bands (15-90 Hz 55-150 Hz 100-250 Hz 200-450 Hz 400-800 Hz). Heart sounds S1 and S2 are detected using amplitude envelopes in the band 15-90 Hz. The goal was to decide if the recording refers to normal or abnormal heart sounds or if it is not possible to decide (i.e. This paper describes a method for automated discrimination of heart sounds recordings according to the Physionet Challenge 2016. Plesinger, F Viscor, I Halamek, J Jurco, J Jurak, P Heart sounds analysis using probability assessment. A technique based on adaptive signal decomposition is developed to In certain pathologies such as the ASD, the split becomes fixed over the respiration cycle.
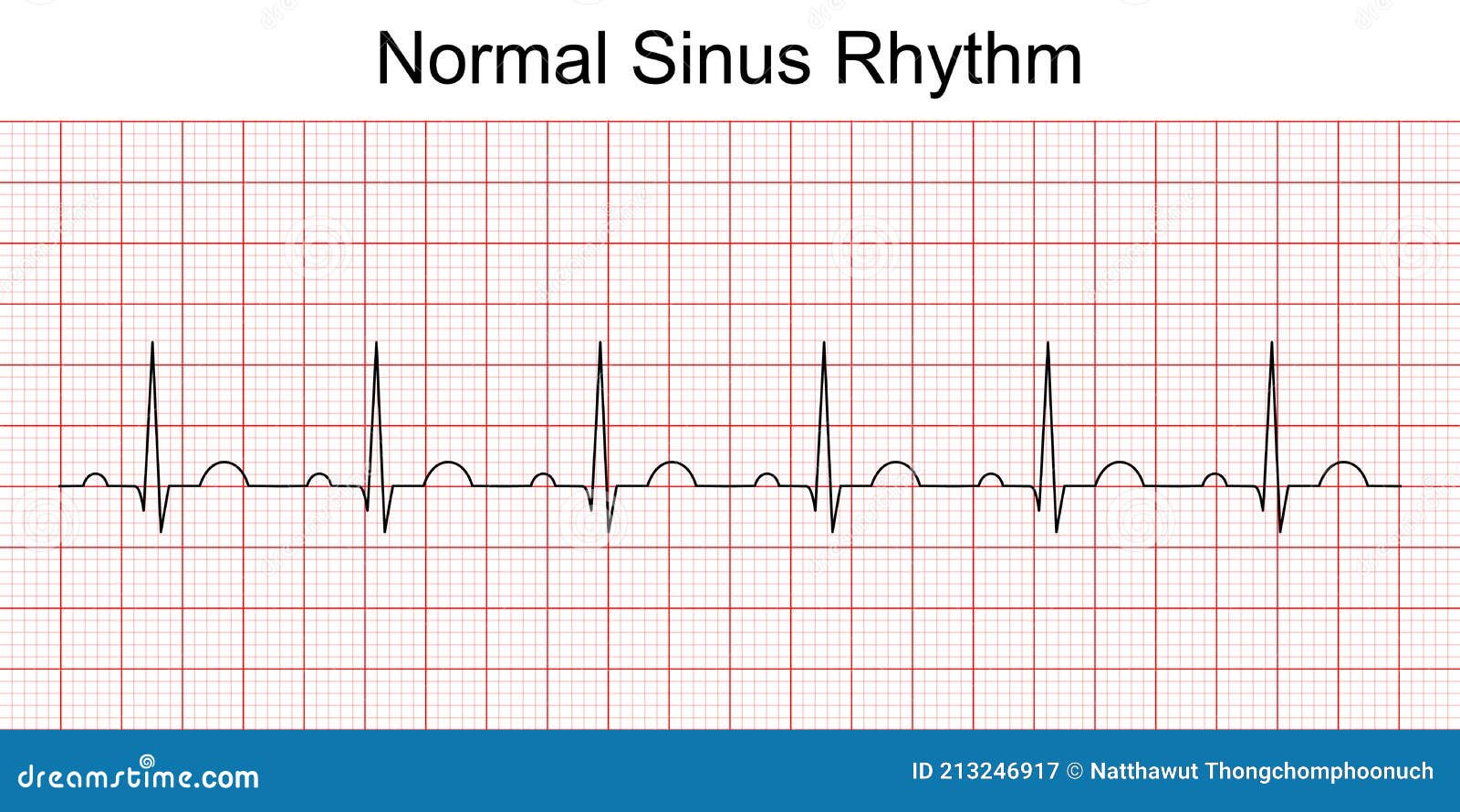
The split normally varies in duration over the respiratory cycle. The aortic valve usually closes before the pulmonary valve, introducing a time delay known as 'split'. The second aspect of the research is to identify splitting patterns in the second heart sound, which consists of two acoustic components due to the closure of the aortic valve and pulmonary valve.
By performing Discriminant Analysis, it was shown that spectral features extracted from the time- frequency representations can be used to distinguish between the three classes. It was found that the three classes of murmurs exhibited different signatures in their time-frequency representations. Modern time-frequency methods including, the Wigner-Ville Distribution, Smoothed Pseudo Wigner-Ville Distribution, Choi-Williams Distribution and spectrogram have been applied to characterise the murmurs. The first aspect of this work is to characterise the three types of murmurs in the time- frequency domain. The acoustic quality of the murmurs generated in each heart condition are different.
They can be found in patients with both pathological and non-pathological conditions.

Murmurs are sounds generated by turbulent flow of blood in the heart. The analysis is based on 42 paediatric heart sound recordings. Two aspects of heart sounds have been specifically investigated the time-frequency analysis of systolic murmurs and the identification of splitting patterns in the second heart sound. This thesis aims to characterise the heart sounds of three groups of children who either have an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD), a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD), or are normal. Structural defects or malfunction of the heart valves will cause additional abnormal sounds such as murmurs and ejection clicks. The operation of the heart can be monitored by the sounds it emits. Time-frequency characterisation of paediatric heart sounds Experience thus far indicates that the PLATO program resources allow the maximum development of the student's proficiency in auscultation. The computer is being used in an innovative manner to teach the recognition of normal and abnormal canine heart sounds at the University of Chicago. Teaching Recognition of Normal and Abnormal Heart Sounds Using Computer-Assisted InstructionĮRIC Educational Resources Information Center


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
